30 - Droughts

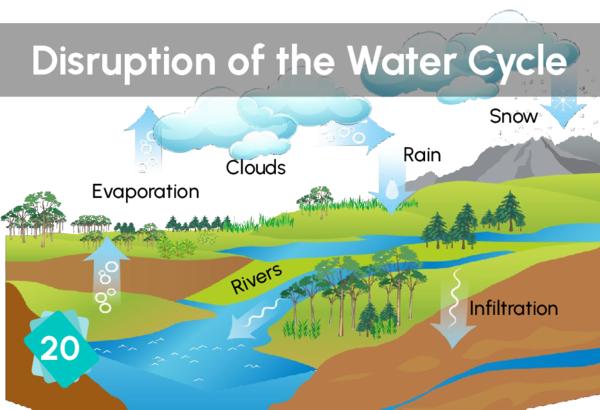
A drought is a period of abnormal water shortage. A meteorological drought is when there is a drop in rainfall, and an agricultural drought is when soil moisture drops abnormally, affecting crop production. A mega-drought is a persistent and widespread drought that lasts much longer than normal (usually a decade or more). Lack of rainfall and evaporation from the ground are the causes of droughts, as well as soil erosion.
Earth from Space
The ESA Sentinel-3 mission reveals how the colour of our vegetation has changed in just one month during the July 2018 drought. These two images cover the same area: part of Ireland, the UK, the Netherlands, Belgium, part of Germany and part of France, but the difference between them couldn’t be more striking. The first, captured on 28 June 2018, is predominantly green, depicting healthy vegetation. The second, captured on 25 July 2018, however, is mainly brown, showing just how much the vegetation has changed owing to the long hot dry spell Europe has been enduring over the last weeks. These two images were captured by Sentinel-3’s ocean and land colour instrument.
Credits :© Copernicus Sentinel data (2018), processed by ESA
1Cause
3Consequences
2Other possible causes
Heatwaves can cause droughts. They often go together.
Deforestation can be the direct cause of droughts because trees stock a lot of water. If they are cut down, they no longer play their part as humidity regulators.